We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on + 1-866 272 8822 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Since data is the most important asset in the digital age, data protection becomes a top priority. One of the ways in which organisations can enhance their ways and methods of data protection and data security is through Network Penetration Testing (NPT). In this blog you will learn all about NPT —examples, techniques, methodology, advantages, and limitations. So, read ahead to learn more!
Table of Contents
1) What is Network Penetration Testing?
2) Phases of Network Penetration Testing
3) Network Penetration Testing tools
4) Network Penetration Testing methodologies
5) Benefits and limitations of Network Penetration Testing
6) Steps to conduct a Network Penetration Test
7) Challenges in Network Penetration Testing
8) Conclusion
What is Network Penetration Testing?
Network Penetration Testing (NPT) is a particular kind of Cybersecurity activity that organisations impersonate the real-time cyberattacks on their systems, networks, applications and applications to test and to make sure the resilience of their critical infrastructures. The main purpose of NPT is to discover sensible interfaces which may be exploited by hackers. It empowers the agencies in detecting weak networks and help them improve their preparedness against a cyber-attack by giving them the opportunity to experience different attack scenarios:
a) Weak passwords
b) Software vulnerabilities
c) Misconfigurations
This forward-looking approach strengthens defences, prioritises remediation efforts and improves overall Cybersecurity strategies; thus, keeps data safe and maintains the integrity of digital assets.
Phases of Network Penetration Testing
Now that you know what exactly Network Penetration Testing means, let's further dig into different phases connected with it. An NPT is a process with several stages, each with a fundamental goal: to identify and address security vulnerabilities. Let’s take a closer look at each stage:
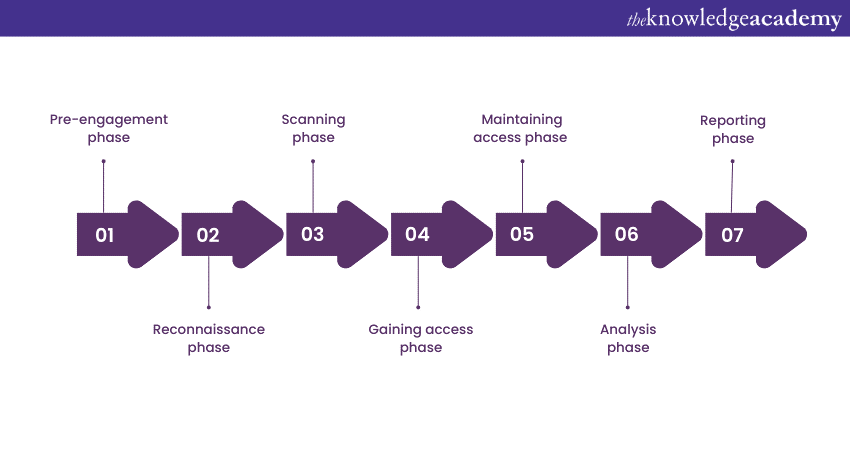
Pre-engagement phase
Pre-engagement is the stage prior to the actual testing that outlines the scope, goals, and engagement for the penetration test. This stage lays the foundation for the whole testing process and sets expectations for the Penetration Testing team and client.
Reconnaissance phase
At this stage, the Penetration Testers collect data about the targeted network and its infrastructure. This data can include domains, IP addresses, network structure, and entry points. The aim here is to mimic the behaviour of attackers who collect information prior to launching an attack.
Scanning phase
The scanning stage may use Nmap among other tools to gather information about the total number of hosts that are active, the number of open ports, and the services that are in operation on the network. A Penetration Tester is tasked with knowing entry points and the attack surface on the network.
Gaining access phase
At this key stage, Penetration Testers try to find weaknesses to get into the target network. These can include weak passwords, unsecured software, or poorly configured systems. The goal is to show how an attacker can break into the network.
Maintaining access phase
After gaining initial access, testers work on maintaining a persistent foothold within the network. This phase demonstrates the potential consequences of an attacker establishing long-term control over compromised systems.
Analysis phase
Throughout the course of the Penetration Test, vulnerabilities, attack paths, and security countermeasures are picked-up and reviewed. The findings can measure the success of the penetration test and offer precise actions to be taken to maintain high information security.
Reporting phase
Once the testing is finished, a thorough report is created that outlines the results, the techniques used, and the weaknesses identified. The report provides a view of the network’s security vulnerabilities and ranks them according to their importance. It also includes suggestions to address the identified weaknesses.
Network Penetration Testing tools
Network Penetration Testing involves simulating cyberattacks to identify vulnerabilities before malicious hackers can exploit them. NPT tools are essential for this process, providing the means to probe, analyse, and secure networks. These tools include the following:
a) Netsparker is a prominent automatic web application scanner designed for Penetration Testing. It’s known for detecting vulnerabilities accurately and reducing false positives.
b) Wireshark, previously Ethereal, is an award-winning network protocol analyser. It allows deep inspection of hundreds of protocols, live capture, and offline analysis.
c) Metasploit is widely recognised as the most utilised Penetration Testing framework globally. It aids Testers in developing and executing exploit code against a remote target machine.
Web Browser Penetration Testing (BEF) is a tool paticularly made for web browser Penetration Testing. It tests a target environment’s actual security posture by using client side attack vectors.
Cain & Abel is a password recovery tool that has been produced for all Windows operating systems. It is an instrument that can be employed to recover a lot of password hashes. As an illustration, it can be leveraged to inspect the network or decrypt encrypted passwords etc.
White-hats Penetration testers are the team of troubleshoot issues caused by the techniques used by black hats hackers used by Pen Testers. For example, Intruder, Zenmap and so many other tools make the process easier.
Network Penetration Testing methodologies
NPT employs various methodologies and approaches to ensure a thorough assessment of a network's security. These methodologies dictate how testers interact with the network and simulate different attacker scenarios. Here are the key methodologies used in Network Penetration Testing:
Black box testing
Black box testing simulates a person trying to hack into a target network without having any prior knowledge of the target networks. The testers rarely get any information about the network such as the name or the URL. Hence, they have to start finding the flaws from the ground. This touches upon the reenactment of attacker's actions and the testing of a network's resilience to threats that may not be obvious.
White box testing
In White box testing, testers have comprehensive knowledge about the target network's infrastructure, architecture, and application code. This approach enables a deep dive into the network's vulnerabilities, as testers can pinpoint weaknesses with precision. White box testing is particularly useful for assessing internal security measures and validating specific issues.
Grey box testing
Grey box testing strikes a balance between Black box and White box approaches. Testers have some partial knowledge of the network, such as basic network architecture or application details.
This allows testers to focus on specific areas of concern while still simulating an attacker with limited knowledge. Grey box testing is often chosen to test a network's response to attackers with some insider information.
Learn the basics of Ethical Hacking with the Ethical Hacking Professional Course!
Benefits and limitations of Network Penetration Testing
There are many benefits to Network Penetration Testing in improving your organisation’s Cybersecurity posture. However, there are also some disadvantages to keep in mind. Let’s take a closer look at the pros and cons of NPT:
Benefits of Network Penetration Testing
The following are some of the benefits of NPT:
1) Vulnerability identification: Vulnerability Scanning is a way of exposing the vulnerabilities that would have otherwise gone unnoticed in traditional security testing. They can use this to pinpoint the weak points and solve those first problems that malicious actors exploit.
2) Real-world simulation: By employing the technique of Penetration Testing you can perform attack simulation scenario, which will provide you with a real-life experience of security of your network. This also provides you with a grasp of how to be responsible in terms of attack and mitigation.
3) Risk prioritisation: The results of Network Penetration Testing are assessed by severity order. This enables businesses to rank remediation efforts based on the most prominent vulnerabilities from their inventory, which could potentially become a gateway to large scale breach.
4) Compliance and regulations: In an increasing amount of cases, there is a wide range of regulation industry requirements for security assessments. Penetration Testing helps in satisfying requirements of compliance standards and avoid unwanted prosecution and penalisation.
5) Trust building: Showing a strong Cybersecurity environment by regularly using Penetration Testing is a way to earn customers trust and faith in an organisation’s capacity to keep protected information safe from attacks.
6) Improvement of defences: The outcomes of a Penetration Testing initiates an action plan for the improvement of the existing security measures, which is ultimately leads to increased security standings of the organisations.
Gain skills of Penetration Testing and securing network from attacks with our Tools And Techniques For Penetrating Testing Course – join now!
Limitations in Network Penetration Testing
Network Penetration Testing has its share of limitations as well, some of which can be highlighted as follows:
1) Time and cost: Penetration Testing can be time-consuming and resource-intensive. Engaging skilled Testers, setting up testing environments, and conducting thorough assessments can be costly.
2) Partial coverage: Penetration Testing covers a subset of vulnerabilities that are discovered during the testing period. It's possible that certain vulnerabilities remain undetected, leading to a false sense of security.
3) Temporary snapshot: Penetration Testing provides a snapshot of the network's security posture at a specific point in time. Changes in the network after testing may introduce new vulnerabilities.
4) Human error: Penetration Testing relies on human expertise, which can be influenced by the tester's knowledge and experience. Overlooking potential attack vectors or making incorrect assumptions can affect the accuracy of the results.
5) Impact on production: In some cases, aggressive testing methods can disrupt network operations, causing downtime or affecting the availability of services.
6) Ethical considerations: Ethical issues are inevitable when testers unknowingly damage classified resources, unauthoritative access fenced data or mismanage valuable assets. Ethic should be tapped into in all development and testing processes.
Challenges in Network Penetration Testing
Penetration testing poses several challenges for Small and Medium-sized Businesses (SMBs), hindering their efforts to bolster Cyber Security. These challenges include the following:
a) Lack of standardised testing procedures: SMBs often get inconsistent results because of the lack of reliable methodology for testing being standardised. Applying standardised testing methods or accepting popular frameworks usually save the process of making of tests and they can be effective as well.
b) Inadequate testing coverage: Insufficient testing across attack vectors can create false security impressions. Conducting comprehensive tests and regular assessments ensures thorough coverage and adaptability to evolving threats.
c) Testing interference with business operations: Penetration Tests sometimes disrupt operations, causing downtime and productivity loss. Scheduling tests during off-peak hours and communicating with stakeholders minimise disruptions.
d) Difficulty measuring testing effectiveness: It's challenging to gauge tests' efficacy. Establishing clear objectives and utilising metrics like vulnerability count and remediation time help evaluate testing effectiveness.
e) Limited resources: SMBs often face resource constraints, hindering comprehensive testing. Prioritising testing objectives based on criticality and outsourcing to specialised firms optimise resource allocation.
f) Lack of in-house expertise: Inadequate internal expertise limits effective testing. Hiring certified professionals or investing in staff training enhances testing capabilities.
g) Limited access to tools and technology: Costly testing tools restrict SMBs. Utilising open-source tools provides cost-effective alternatives for identifying vulnerabilities.
h) Complex network infrastructure: SMBs with intricate networks struggle to identify attack entry points. Mapping network infrastructure and using automated scanning tools streamline testing.
i) Limited time for testing: Time constraints compromise thorough testing. Prioritising objectives and employing automation maximising testing efficiency within time limits.
j) Lack of buy-in from management: Management's indifference to testing undermines efforts. Educating them on the importance of testing and presenting findings persuasively secures necessary support.
k) Lack of awareness among employees: Employee actions can compromise security. Funding security awareness programs and conducting social engineering tests mitigate risks posed by employee behaviour.
l) Limited remediation resources: Addressing identified vulnerabilities strains SMB resources. Prioritising high-risk vulnerabilities and investing in cost-effective solutions optimise remediation efforts.
Conclusion
To sum it up, Network Penetration Testing stands as a crucial shield against rapidly growing cyber threats. This Cybersecurity measure helps empower organisations by revealing weaknesses and giving actionable insights into ways to strengthen their defences. Organisation must keep in mind that this is not a common practice of testing; this is a kind of commitment to having strong security, which provides a safer world in the digital environment.
Try our Ethical Hacking Training and learn to bypass the security of systems legally!
Frequently Asked Questions

The Network Penetration Test is a simulated check of a computer network against exposure to vulnerabilities and weaknesses in regard to cyberattack. In such a test, skilful professionals, known as Ethical Hackers—try to get the best of security flaws to fairly verify the resilience of systems.

Penetration Testing network involves simulating cyberattacks on a system to identify vulnerabilities and assess its security. It typically follows a systematic process, including reconnaissance, scanning, gaining access, maintaining access, and analysis. Ethical hackers use various tools and techniques to exploit weaknesses, providing insights for organisations to strengthen their defenses against real threats.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Automation & Penetration Testing Courses, including Tools and Techniques for Penetrating Testing, Fundamentals of Test Automation etc. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into how to become a Cyber Security Expert.
Our IT Security & Data Protection Blogs covers a range of topics related to Fundamentals of Test Automation, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your IT skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming IT Security & Data Protection Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Fundamentals of Test Automation
Fundamentals of Test Automation
Fri 10th Jan 2025
Fri 14th Feb 2025
Fri 11th Apr 2025
Fri 13th Jun 2025
Fri 8th Aug 2025
Fri 26th Sep 2025
Fri 21st Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


