We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +27 800 780004 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Imagine a retail company struggling to understand why certain products aren’t selling as expected. Given such a situation, they can gather huge amounts of information from various sources by harnessing Big Data. However, understanding the difference between Big Data and Business Intelligence is crucial for any organisation aiming to stay competitive. Moreover, Statista, states that the total amount of data created, collected, copied and consumed globally will be approximately more than 180 zettabytes by 2025.
Considering such circumstances, this blog will take you through the significant differences between Big Data and Business Intelligence. Dive in to know more!
Table of Contents
1) Big Data and Business Intelligence: An Overview
2) What is the difference between Big Data and Business Intelligence?
a) Conceptual definition
b) Nature and composition
c) Purpose and objectives
d) Technological aspects
e) Analysis depth
3) Is Big Data Better Than Data Science?
4) Conclusion
Big Data and Business Intelligence: An Overview
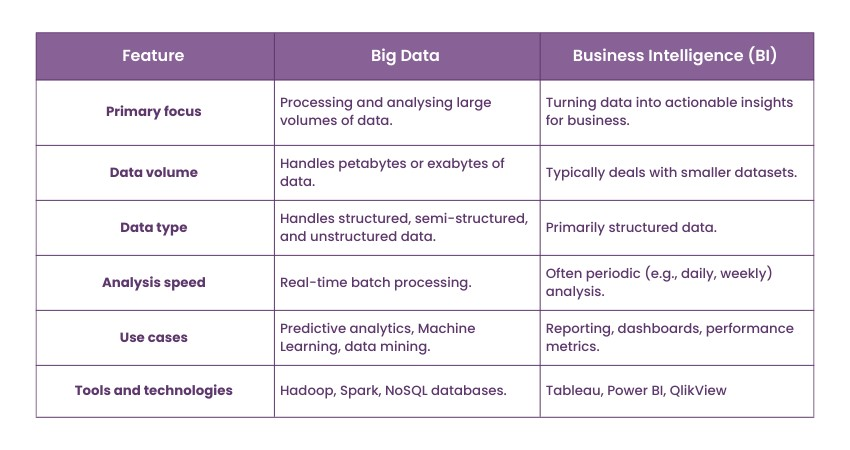
Big Data denotes the vast and complex datasets that traditional data processing tools struggle to manage. This data is characterised not only by its immense volume but also by its variety, velocity, and veracity. It originates from diverse sources such as social media, sensors, and machines, arriving at high speeds and in various formats—structured, semi-structured, or unstructured. The main challenge and opportunity with Big Data lie in not just collecting it but also in extracting valuable insights from it.
Business Intelligence (BI) encompasses the methodologies, processes, architectures, and technologies that transform this massive data into understandable and actionable information for businesses. BI tools help visualise data, creating reports, dashboards, and other analytical tools to derive actionable insights. While Big Data provides the raw material, BI shapes it into valuable insights, bridging the gap between data potential and actionable business strategies.
What is the Difference Between Big Data and Business Intelligence?
Here are some major differences between Big Data and Business Intelligence that can help you understand these terms better:
1) Conceptual Definition
The term Big Data is derived from the challenges and opportunities associated with processing and analysing vast amounts of data. It is characterised by the three Vs:
a) Volume (amount of data)
b) Velocity (speed at which new data is generated)
c) Variety (different types of data)
Recently, other Vs like Veracity (quality and accuracy of data) and Value (usefulness of the data) have been added to its definition. Big Data can come from social media, Internet of Things (IoT) devices, transactional databases, logs, and many other sources.
On the other hand, BI is the process, technology, and practices for the collection, integration, analysis, and visualisation of business information. The main purpose of BI is to support better business decision-making. It often uses processed and structured data from Big Data sources and turns it into actionable insights through various tools and techniques.
2) Nature and Composition
Big Data encompasses both structured and unstructured data. Structured data is well-organised and easily queried using standard database systems (e.g., relational databases). Unstructured data, on the other hand, is more chaotic and doesn't fit neatly into traditional database categories (e.g., texts, videos, and social media posts).
On the contrary, Business Intelligence primarily deals with structured data. The tools and processes in BI are specifically designed to handle data that's already been cleaned, categorised, and structured.
3) Purpose and Objectives
Big Data’s primary aim is to store and manage a massive amount of diverse data efficiently. Big Data solutions are geared towards ensuring that data is accessible, regardless of its size or type.
Whereas the core purpose of Business Intelligence is data interpretation. BI aims to use the available data to generate reports, make predictions and spot market trends. It also identifies business problems and opportunities and ultimately guides strategic business moves.
Stay ahead of the curve by joining our Advanced Data Analytics Course – book your spot now!
4) Technological Aspects
Big Data Integration relies heavily on technologies like Hadoop, Spark, and NoSQL databases. These technologies are adept at storing and processing enormous data sets across distributed computing environments.
On the other hand, Business Intelligence is a rich history of tools and solutions, ranging from traditional data warehousing solutions to modern dashboard tools. It includes tools like Tableau, Qlik, and Power BI. These tools assist in data visualisation, reporting, and analytics.
5) Analysis Depth
Big Data can be incredibly deep, utilising advanced methods like Machine Learning, Artificial Intelligence, and Deep Learning to discern patterns in massive datasets.
Whereas, Business Intelligence typically employs descriptive analytics, which looks at historical data to understand past behaviours. This includes generating regular business reports, Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) tracking, and other retrospective analyses.
6) Time Orientation
With its ability to process real-time streams of data (often called "streaming data"), Big Data solutions can be oriented towards both historical and real-time data. In contrast, Business Intelligence traditionally focuses on historical data to inform current decisions. However, with the evolution of BI tools and the integration of Big Data, some modern BI solutions can now handle real-time Data Analytics.
7) Users
Typically, Data Scientists, Data Engineers, and Information Technology specialists are the main users of Big Data. They have specialised knowledge and skills to handle and process vast amounts of diverse data.
Whereas Business Analysts, managers, and decision-makers are the primary users of Business Intelligence. BI tools are designed to be more user-friendly, allowing those without deep technical knowledge to generate reports, dashboards, and insights.
8) End Goal
Big Data aims at efficient data storage, processing, and preliminary analysis. The end goal is to have data in a ready state from which detailed insights can be derived. On the contrary, the end goal of BI is actionable intelligence. Whether it's understanding customer behaviours, optimising operations, or predicting sales, BI turns data into information that can directly support business actions and strategies.
Empower your decisions with clarity – register for our Business Intelligence Reporting Training now!
9) Infrastructure and Scalability
As Big Data involves managing vast amounts of data, its infrastructure often leans towards distributed systems, where data is stored across several machines or even across data centres. These systems, like Hadoop clusters, are designed for horizontal scalability, meaning they can expand by adding more nodes to the system. This modularity ensures that as data grows, the system can scale out to accommodate the increasing load.
However, BI systems are traditionally operated on single, powerful servers or dedicated data centres. They began integrating with Big Data sources and cloud technologies when the infrastructure evolved. Today, many BI tools support cloud integration, offering flexible and scalable solutions that leverage the power of distributed processing.
10) Data Quality and Management
With such vast quantities of data coming in from varied sources, ensuring data quality can be a significant challenge in Big Data environments. Data can be messy, inconsistent, or even redundant. Therefore, Big Data solutions often incorporate data cleaning, data wrangling, and data management tools.
On the contrary, even before reaching to BI tools, data usually undergoes rigorous cleaning and transformation processes. BI relies on the accuracy and reliability of data, as insights derived from it directly influence business decisions.
11) Security concerns
With the sheer volume and diversity of data, security in Big Data environments can be challenging. Ensuring data privacy, especially with data coming from varied sources and often containing personal information, is paramount.
Since BI tools are often used to generate reports and dashboards for decision-makers, they incorporate robust security features. These tools ensure that sensitive business information is only accessible to authorised individuals and is presented in a secure manner.
Discover insights from the depths of data with our Big Data Analysis Course - join us now!
Is Big Data Better Than Data Science?
Big Data and Data Science are two pivotal fields in the realm of Data Analytics, each with its unique strengths and applications. While Big Data provides the raw material, Data Science offers the tools and expertise to turn this data into actionable insights. Here are some key differences:
a) Scope: Big Data focuses on handling and processing large datasets, whereas Data Science is concerned with extracting knowledge from data, regardless of its size.
b) Tools and Techniques: Big Data relies on technologies like Hadoop and Spark, while Data Science uses Machine Learning, Statistical Analysis, and Data Visualisation tools.
c) Applications: Big Data is crucial for industries that deal with massive amounts of data, such as social media, finance, and healthcare. Data Science is applied across various domains to solve complex problems and make data-driven decisions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the difference between Big Data and Business Intelligence is crucial. While Big Data offers a treasure trove of raw information, Business Intelligence transforms it into actionable insights. Together, they can empower businesses to innovate and thrive in a data-driven landscape.
Illuminate your business decisions with our Business Objects Reporting Course. Register today!
Frequently Asked Questions

Business Intelligence (BI) and Big Data both aim to analyse data for better decision-making. They involve data collection, processing, and visualisation to provide insights. Both use analytical tools and techniques to identify patterns, trends, and opportunities, ultimately supporting strategic business decisions.

To extract Business Intelligence from Big Data, first gather and store relevant data. Next, cleanse and organise it for analysis. Apply analytical tools to identify patterns and trends, then visualise the results. Finally, interpret the findings to guide data-driven decision-making and improve business strategies.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Big Data and Analytics Trainings, including the Advanced Data Analytics Course, Data Analytics With R Course, and Big Data Analysis Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into What is Couchbase.
Our Data, Analytics & AI Blogs cover a range of topics related to Big Data and Analytics, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Data, Analytics and Artificial Intelligence (AI) skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Data, Analytics & AI Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Hadoop Big Data Certification
Hadoop Big Data Certification
Thu 23rd Jan 2025
Thu 20th Mar 2025
Thu 22nd May 2025
Thu 17th Jul 2025
Thu 18th Sep 2025
Thu 20th Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


