We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +44 1344 203 999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Decision Making is an integral part of our daily lives, whether we're deciding what to eat for breakfast or steering a business through a major strategic shift. Every choice we make shapes the path ahead, but how often do we stop to truly think about the process behind these decisions? What is Decision Making, and why is it such a critical skill?
In this blog, we’ll dive into the fascinating world of Decision Making, exploring the various steps involved and understanding the types of decisions we encounter. By examining these aspects, we will uncover What is Decision Making truly entails, which is the first step toward mastering it. Let’s get started!
Table of Contents
1) What is Decision Making?
2) Steps of the Decision Making Process
3) Types of Decisions
4) What Can Prevent Effective Decision Making?
5) Factors Influencing Decision Making
6) Conclusion
What is Decision Making?
Decision Making meaning refers to the process of selecting a course of action from various alternatives to achieve a desired outcome. It involves identifying options, evaluating their potential consequences, and choosing the best path forward. This process is vital in both personal and professional contexts, helping individuals and organisations navigate challenges and seize opportunities.
Effective Decision Making leads to successful outcomes, while poor Decision Making can result in negative consequences. By carefully considering options and potential impacts, decision makers can make informed choices that align with their goals and values.
Steps of the Decision Making Process
The Decision Making process typically involves several steps:
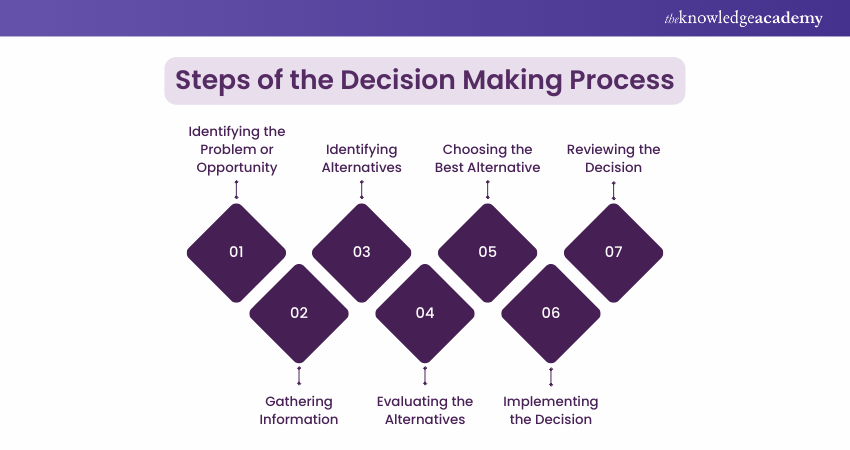
1) Identifying the Problem or Opportunity
a) Start by identifying the problem you need to solve or the question you need to answer.
b) Define the decision clearly and ensure the problem is specific and not too broad.
c) If there’s a specific goal tied to the decision, make it measurable and time-bound.
2) Gathering Information
a) Collect all necessary data related to the decision, including internal assessments of past successes and failures.
b) Seek insights from external sources like studies, market research, or consultants if needed.
c) Be careful about information overload, as too much data can complicate the Decision Making process.
3) Identifying Alternatives
a) With the gathered information, outline all possible solutions or courses of action.
b) Consider different strategies to meet your goal. For instance, if the goal is boosting social media engagement, alternatives could include paid ads, refining your organic strategy, or using a combination of both.
4) Evaluating the Alternatives
a) Evaluate the pros and cons of each alternative.
b) Examine similar scenarios from other organisations and review your own company’s history of wins and losses.
c) Identify the risks and rewards associated with each option and consider potential pitfalls.
5) Choosing the Best Alternative
a) After analysing all the alternatives, make your decision.
b) Ensure you’ve clearly defined the decision, reviewed all relevant information, and thoroughly weighed each potential option.
6) Implementing the Decision
a) Implement the decision by creating a detailed action plan.
b) Assign specific tasks to your team members to execute the plan and ensure the decision becomes a reality.
7) Reviewing the Decision
a) After a set period of time (established in the first step), review the outcome of your decision.
b) Reflect on whether you solved the problem, answered the question, or met the goals.
c) If successful, note the key factors for future decisions. If not, learn from any mistakes and refine the process for next time.
Master Agile Leadership Training – elevate your Leadership journey today!
Types of Decisions
Now that we’ve covered the Decision Making Process, it’s important to understand the different types of decisions one may face in life. Decisions can be categorised based on factors such as complexity, impact, and time frame. Let’s explore each of these decision types in detail:
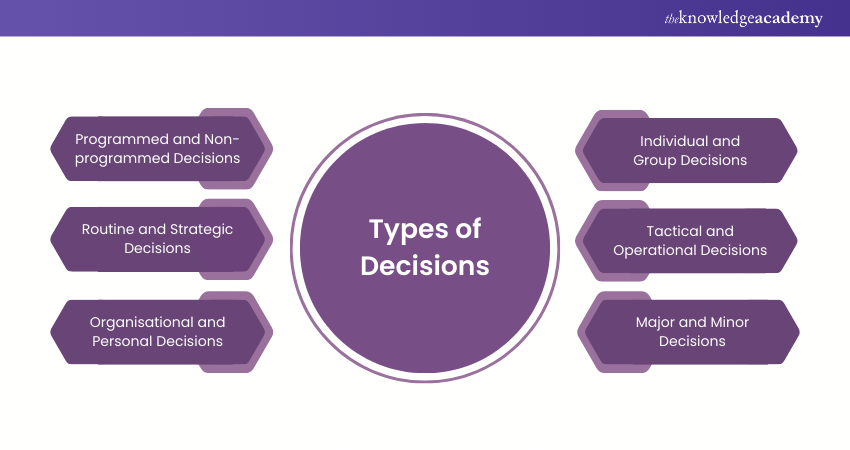
1) Programmed and Non-programmed Decisions
Programmed Decisions:
a) Address routine repetitive problems
b) Use established methods and procedures
c) Simple, short-term, and made by lower-level managers
d) Example: Handling employee tardiness using a standard disciplinary process
Non-programmed Decisions:
a) Deal with unique, complex issues requiring executive judgment
b) No predefined solutions; require creative problem-solving
c) Made by higher-level managers
d) Example: Deciding to launch a new product or choosing a factory location
2) Routine and Strategic Decisions
Routine Decisions:
a) Repetitive and related to day-to-day operations
b) Short-term, handled by lower-level management using established procedures
c) Example: Deciding on employee overtime payments
Strategic Decisions:
a) Long-term involves significant investment and planning
b) Impact the future direction of the organisation
c) Made by higher management
d) Example: Entering a new market or implementing major organisational changes
3) Organisational and Personal Decisions
Organisational Decisions:
a) Made by managers in their official capacity as resource allocators
b) Directly impact the organisation’s functioning
c) Can be delegated
d) Example: Allocating resources for a new project
Personal Decisions:
a) Made by managers in their individual capacity
b) Related to personal matters and cannot be delegated
c) It may indirectly impact the organisation
d) Example: A manager deciding to retire early, affecting company succession planning
4) Individual and Group Decisions
Individual Decisions:
a) Made by a single person based on available information
b) Quick and often straightforward
c) Example: A manager deciding on a budget allocation for a department
Group Decisions:
a) Involve input from multiple people, often made by committees or boards
b) Encourage diverse perspectives but may cause delays
c) Example: A Board of Directors making decisions on company mergers
5) Tactical and Operational Decisions
Tactical Decisions:
a) Focus on short-term actions to implement broader strategies
b) Made by middle management
c) Example: Deciding on a marketing campaign to boost sales next quarter
Operational Decisions:
a) Concern routine day-to-day activities and procedures
b) Short-term and handled by lower-level managers or supervisors
c) Example: Creating daily work schedules for employees
6) Major and Minor Decisions
Major Decisions:
a) Significant, long-term decisions that can affect life or business outcomes
b) Requires careful thought, research, and often external advice
c) Example: Deciding on a career path or buying a house
Minor Decisions:
a) Small, everyday choices with short-term impacts
b) Made quickly with minimal deliberation
c) Example: Deciding what to eat for lunch or which movie to watch
Try our Successful People Management and Team Leadership Course today and take your organisation to a new height!
What Can Prevent Effective Decision Making?
Several factors can prevent effective Decision Making. Here are some common obstacles:
a) Lack of Information: Insufficient or inaccurate information can lead to poor decisions. It’s crucial to gather all relevant data before making a decision.
b) Overload of Information: Conversely, having too much information can be overwhelming and lead to analysis paralysis, where Decision Making is delayed due to overthinking.
c) Emotional Influence: Emotions like fear, anger, or excitement can cloud judgment and lead to biased decisions. It’s important to remain objective and rational.
d) Time Constraints: Limited time can pressure decision-makers to rush, potentially leading to hasty and poorly thought-out decisions.
e) Complexity of the Problem: Highly complex problems can be difficult to analyse and solve, making it challenging to arrive at an effective decision.
f) Lack of Resources: Insufficient resources, such as time, money, or personnel, can limit the options available and affect the quality of the decision.
g) Resistance to Change: Organisational or individual resistance to change can prevent the implementation of effective decisions, even if they are well-made.
h) Poor Communication: Miscommunication or lack of communication can lead to misunderstandings and errors in Decision Making.
i) Cognitive Biases: Biases such as confirmation bias, anchoring, and overconfidence can distort perception and lead to flawed decisions.
j) Groupthink: In group Decision Making, the desire for harmony and conformity can suppress dissenting opinions and lead to suboptimal decisions.
k) Lack of Clear Objectives: Without clear goals or objectives, it can be difficult to evaluate options and make a decision that aligns with desired outcomes.
l) Inadequate Risk Assessment: Failing to properly assess risks can result in decisions that are either too risky or too conservative.
Enhance your organisational efficiency through our Decision Making Course – register today!
Factors influencing Decision Making
Decision Making is influenced by several factors. Understanding these factors is crucial as they impact the quality and rationality of decisions made. Let's explore some key influences on Decision Making:
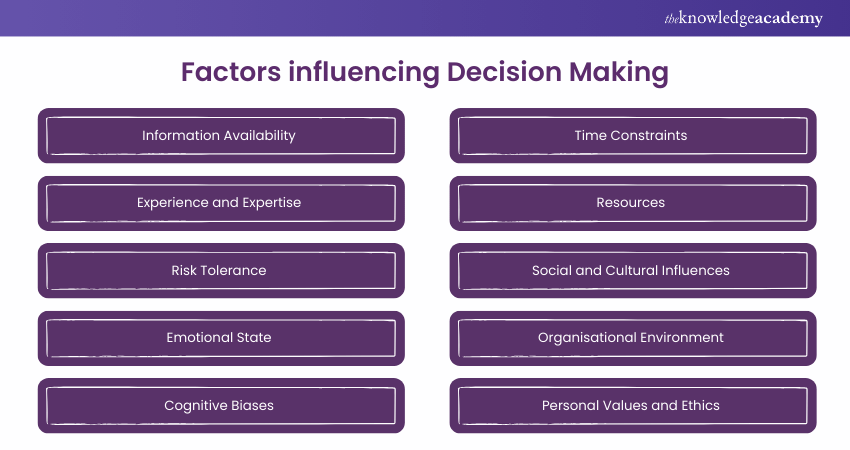
a) Information Availability: The quality and quantity of information available can significantly impact the Decision Making process. Accurate and comprehensive data helps in making informed decisions.
b) Experience and Expertise: Past experiences and the level of expertise of the decision-maker play a crucial role. Experienced individuals can draw on their knowledge to make better decisions.
c) Risk Tolerance: Different individuals and organisations have varying levels of risk tolerance. This affects how they approach decisions, especially those involving uncertainty or potential negative outcomes.
d) Emotional State: Emotions such as stress, anxiety, or excitement can influence Decision Making. It’s important to manage emotions to maintain objectivity.
e) Cognitive Biases: Biases like confirmation bias, anchoring, and overconfidence can distort judgment and lead to flawed decisions.
f) Time Constraints: The amount of time available to make a decision can affect its quality. Rushed decisions may not be as well-considered as those made with ample time.
g) Resources: Availability of resources such as time, money, and personnel can limit or expand the options available for Decision Making.
h) Social and Cultural Influences: Social norms, cultural values, and peer pressure can impact decisions, especially in group settings.
i) Organisational Environment: The culture, structure, and politics within an organisation can influence Decision Making processes and outcomes.
j) Personal Values and Ethics: An individual’s personal values and ethical standards play a significant role in shaping their decisions.
k) External Environment: Factors such as economic conditions, technological changes, and regulatory requirements can influence Decision Making.
l) Stakeholder Input: Feedback and opinions from stakeholders, including employees, customers, and investors, can impact the Decision Making process.
Be a great leader through our Leadership Skills Course - sign up now!
Conclusion
Understanding What is Decision Making is essential for both personal and professional growth. By mastering the steps and understanding the factors that influence our choices, we can sharpen our Decision Making skills. This foster better outcomes in both our personal lives and organisations. Let’s embark on this empowering journey toward informed and impactful decisions!
Try our Introduction to Supervising a Team Course and gain excellence in supervision!
Frequently Asked Questions

Effective Decision Making enables individuals to identify and pursue diverse job opportunities, leading to better career development. It helps in setting clear goals and evaluating paths for professional growth.

Here are the headings for strategies to enhance Decision Making abilities:
a) Seek Feedback
b) Analyse Past Experiences
c) Collaborate with Colleagues
d) Prioritise Tasks
e) Stay Informed
f) Practice Critical Thinking

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Leadership Courses, including Leadership Skills Course, Agile Leadership Training and Instructional Design Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Delegating Leadership Style.
Our Business Skills Blogs cover a range of topics offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Successful People Management and Team Leadership
Successful People Management and Team Leadership
Fri 10th Jan 2025
Fri 28th Feb 2025
Fri 4th Apr 2025
Fri 16th May 2025
Fri 11th Jul 2025
Fri 19th Sep 2025
Fri 21st Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


