We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +44 1344 203 999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Activities, both in daily life and the workplace include some level of Manual Handling. Therefore, it is important to understand “What is Manual Handling?” It describes the action of lifting, moving, pushing, or pulling something by hand rather than with the use of equipment. We all perform physical handling tasks; however, it becomes very important to know the right technique.
Whatever work you conduct, there is a good likelihood that it will occasionally need Manual Handling. If done incorrectly, can result in a variety of ailments, from muscle strain to severe Musculoskeletal Disorders (MSDs).
It can easily lead to catastrophic short, or long-term injuries. This blog answers “What is Manual Handling?” in conjunction with workplace standards, and the proper planning and execution of Manual Handling procedures.
Table of Content
1) What is Manual Handling?
2) Manual Handling Responsibilities of Employers
3) Manual Handling Responsibilities of Members
4) How to Avoid Manual Handling Injuries?
5) Consequences of Poor Manual Handling Safety
6) Key Principles of Manual Handling Safety
7) Conclusion
What is Manual Handling?
Manual handling is defined as inclined or vertical lifting or lowering or transportation of load by using hand or by bodily strength. Manual handling accidents are the most frequent type of accident in the workplace and the risks associated with manual handling remain a concern for nearly every member.
Consequences arising out of manual handling accidents may assume such serious dimensions that they bring about a permanent change in the personal as well as professional existence of the people involved.
It is not only a problem for workers involved directly with manual handling of items, as nearly every worker can expect to move an object at some point in their work cycle.
Implement Health and Safety in the Workplace and prioritise a healthy work environment today!
Manual Handling Responsibilities for Employers
There are several important duties that employers must meet to safeguard the well-being of the worker when carrying out manual handling operations. These include:
a) Risk Assessment: Employers need to ensure they undertake some risk assessments to have a list of the risks connected with manual handling tasks in a workplace. This should involve factors such as the weight of the load, the position and manner of handling it.
b) Control Measures: According to the risk evaluations, employers must put into practice protective methods regarding risks. This may include adjusting and redesigning workstations, utilising lifting appliances or wherever possible developing ways of moving heavy objects through techniques such as mechanisation.
c) Training and Education: Employers are required to ensure that their employees receive instructions in relation to manual handling of loads in a safe manner. This set of training should correspond to the assignments that the employees will be performing and the tools which they will be utilising.
d) Provide Adequate Equipment: Basic equipment consists of manually operated lifting aids including trolleys and mechanical hoists for manual handling tasks that should significantly reduce physical stress.
e) Encourage Proper Technique: Employers should ensure that employees adhere to proper working postures and lifting practices in order avoid the following such as; Actions that involve the bending part of the back instead of the knee, twisting movements etc.
f) Monitor and Review: This should be done routinely and involve checking tasks involving manual handling and the risk assessments made with a view to having the right measures put in place then updated as required.
g) Health and Safety Support: It makes sure that there is easy visibility of any health and safety concerns and facilitates the filing of complaints on manual handling operations.
h) Promote a Safe Working Environment: A clean and well lit, organised and ergonomic work environment helps prevent Manual Handling risks while helping foster the health of the employees.

Manual Handling Responsibilities for Members
Worker representatives also process some responsibilities to guarantee their safety and the safety of others in completing MH tasks. Their responsibilities include:
a) Follow Training and Instructions: Employers need to ensure members are well trained in the manual handling training that has been put in place for safe handling of items.
b) Use Equipment Properly: When using equipment like trolleys or lifting devices to perform manual handling tasks the employees should ensure they do it correctly to avoid incurring an injury.
c) Report Hazards: Members should provide their employer with any hazards, and faulty or unsafe equipment and conditions as that would lead to accidents.
d) Assess Before Lifting: In general, it is recommended that the workers should – Whenever possible – evaluate and decide if the load can be lifted without causing undue stress to the back muscles.
e) Maintain Proper Technique: Whenever possible, members must abstain from twisting while lifting an object, lifting with the legs rather than the back and holding the object close to the body.
f) Communicate with Team Members: Exercise such as lifts require coordination when handling requires communication during a team lift.
g) Stay Physically Prepared: Some personal preventive measures can be recommended for cutting down on manual handling risks, such as, personal health involving stretching or physical fitness.
Elevate your skills with our comprehensive Health and Safety Training for Managers and Supervisors - Sign up today
How to Avoid Manual Handling Injuries?
All Manual Handling jobs must be thoroughly evaluated and planned before beginning in order to prevent injury. It is necessary to recognise and assess the risks associated with the task. There must be implementation of measures to reduce or eliminate these dangers. Following are some steps that need to be followed to avoid manual handling injuries:
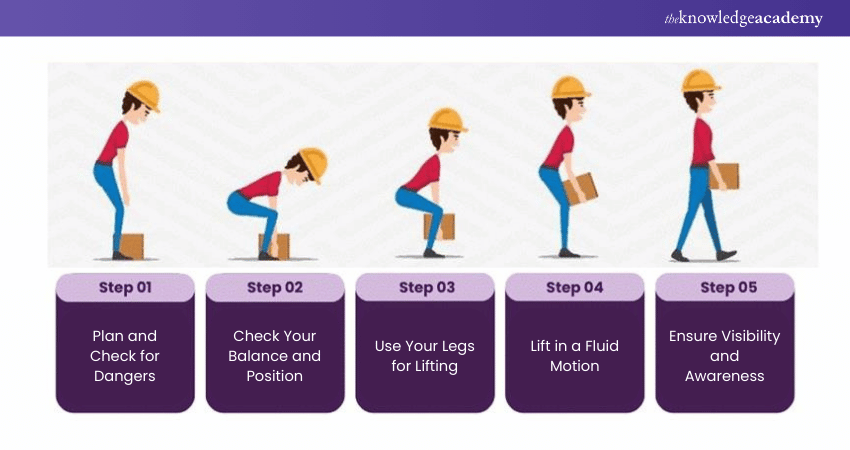
Step 1 - Plan and Check for Dangers:
Learn to look at every single lifting operation you are about to undertake and evaluate it. Note any possible dangers, as well as any shiny, smooth, or damaged surface and any objects in your way. Make sure that the load is going to be steady and also ensure it is not too heavy.
Step 2 - Check Your Balance and Position:
Stand beside the load with your legs more or less apart depending on your height in order to feel balanced. Always make sure that you have a good grip and do not lean in ways that may cause strain to your body. Steady your spine – do not lean forward or backward by keeping your back straight and bearing your weight with your abdomen muscles.
Step 3 - Use Your Legs for Lifting:
The principle here is to bend your knees and not on your stomach; instead, lift with your leg muscles. Your legs are far stronger than your back, reason why they are suitable for supporting the weight of item. Tuck the load in close to your body to reduce compression on your lower spine and avoid too much reaching forward or backward movements.
Step 4 - Lift in a Fluid Motion:
Immobility can easily lead to straining muscles or joints that require being as gently moved as possible. Pick the load with as little jerks as possible and ensure that at no one point are you struggling with it. Make sure your head is up and that your eyes are pointing in the direction of the nose rather than down, this helps keep the spine in alignment.
Step 5 - Ensure Visibility and Awareness:
Ensure that the load is not obstructive, that is you should be able to see where you are going. Look around you and see people, doors and any other object on your path. If it is needed, tell something to colleagues, for example in the common area or during teamwork, when using a tall-lifting device, in order to prevent accidents.
Discover the essential Manual Handling Equipment to improve safety and efficiency. Read our blog to learn more!
Consequences of Poor Manual Handling Safety
Injury arising from improper manual handling technique is a broad category and the majority of the conditions are certain, and involve the muscles, nerves, tendons, joints, or spinal discs. Among the most prevalent are:
a) Back Injuries: Of these, perhaps, the most that can be easily related to poor manual handling are the four that are described in the next section. Lifting that is done improperly may result in strains, sprains, and even such severe problems as herniated discs. Such injuries are normally serious and take a long time to heal.
b) Shoulder and Neck Injuries: Intersecting the lift force and the direction of the force increases the pressure lifted with specific focused stress on the neck and the shoulder muscles, which if handled poorly frequently can result in strain or chronic pain.
c) Repetitive Strain Injuries (RSI): Such injuries are chronic, and they occur as a result of incorrect motions that have been repeatedly made. RSIs can be located almost anywhere in the body and are often very painful.
Explore comprehensive training on Manual Handling At Work to ensure you are equipped with the knowledge to work safely.
Key Principles of Manual Handling Safety
Manual handling safety is crucial to avoid occurrences of injuries in workplaces and homes. While employers may tailor their approaches, manual handling generally involves four key principles: well-coordinated assessment, correct method, skill, time and tools.
a) Assessment: Before moving or lifting an object, the workers should assess the weight, size and how it should be lifted. The suggested training for the appraisal of tasks lets the employees decide whether support from others is required, in terms of tools or more heads, avoiding unrecognised risk.
b) Proper Technique: Safe handling does not require strength and might but rather proper methods when handling stuff manually. The workers should bend the knees, the load should touch the workers’ body and workers should not twist or overextend when lifting the load.
c) Training: Worker training plays a major role in promoting correct manual handling instructions, especially in endangered regions. Confirmations and revision courses guarantee that risky habits are changed hence forgoing the advisory-training- revision cycle; everyone will apply the aspect learned.
d) Equipment: When such tasks require more force, then it is simply impossible to accomplish them with manual strength. Such tools as trolleys, hoists or conveyor belts are made available to minimise pulling and lifting while upping on safety measures.
Conclusion
To minimise injuries and promote workplace safety, it is essential to implement safe Manual Handling procedures. It is important to understand What is Manual Handling? to reduce strain by evaluating worker’s task at hand, thereby removing obstacles from the way, and learning to stand steadily. Prioritising these procedures helps in overall job satisfaction in addition to protecting against immediate injuries.
Want to know more about health and safety? Explore our Health and Safety in Workplace Training - Join today!
Frequently Asked Questions

The golden rule of manual handling is to lift with your legs, not your back. Always bend your knees, keep the load close to your body, and avoid twisting or overreaching. Using proper technique reduces strain, preventing injury and promoting safe lifting practices.

The four stages of manual handling are:
a) Assessment: Evaluate the load and environment.
b) Preparation: Position yourself correctly and plan the lift.
c) Lifting: Use proper technique—bend your knees, not your back.
d) Transport: Carry the load safely to the destination, avoiding strain.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Health and Safety in the Workplace, including the Manual Handling at Work, First Aid at Work and the Working at Height Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Workplace Safety Tips.
Our Health and Safety Blogs cover a range of topics related to Manual Handling, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Health and Safety Skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Health & Safety Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Manual Handling at Work
Manual Handling at Work
Fri 17th Jan 2025
Fri 7th Mar 2025
Fri 23rd May 2025
Fri 18th Jul 2025
Fri 12th Sep 2025
Fri 12th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


