We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +44 1344 203 999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

In the present innovation-focused society, safeguarding intellectual property (IP) is crucial for businesses aiming for a competitive advantage. Developing a thorough Intellectual Property Strategy helps companies protect their innovations, concepts, and blueprints, facilitating their path to monetisation and profit. It is crucial to safeguard and proactively handle intellectual property assets in a way that is in line with the company's vision and market goals.
A successful Intellectual Property Strategy means setting specific objectives, recognising important assets, and creating ways to safeguard, supervise, and use IP. Businesses ranging from new companies to large corporations need to understand the strategic significance of intellectual property and take steps to maximise their intellectual.
Table of Contents
1) Understanding Intellectual Property (IP) Strategy
2) Who needs an IP strategy?
3) Essential Elements of an IP Strategy
4) Basic Steps to a Successful IP Strategy
5) Advantages of a Strong IP Strategy
6) Challenges in Implementing an IP Strategy
7) Conclusion
Understanding Intellectual Property (IP) Strategy
It resembles a business plan, but it concentrates on your Intellectual Property (IP) asset. Brand, trade secrets, data, and know-how are crucial operational assets in numerous businesses, fueling expansion and supporting profit flows. Creating an intellectual property strategy makes sure that the main business plan includes these crucial business assets.
Companies with a strong intellectual property plan that can hold up under scrutiny from potential investors tend to experience quicker growth and are usually more successful in obtaining loans and investments at greater values.
Who Needs an IP Strategy?
Every leadership group or board of directors seeks a strategy to construct or enhance the competitive advantage of the company. The process of developing an IP strategy typically starts with creating a new or updating an already existing formal IP strategy document, which may be a PowerPoint deck.
This document assesses, values, and displays your various IP assets, including patents, trademarks, software, trade secrets, and expertise. It will also outline your strategy for enhancing the strength of these assets, addressing any weaknesses in your IP protection, and demonstrate how this will boost your business growth and set you apart from competitors.
Boost your career with Contract Management Training. Gain valuable expertise in contract negotiation, risk management, and compliance. Start learning now!
Essential Elements of an IP Strategy
The essential elements of an IP strategy are as follows:

Protecting Intellectual Property
Securing intellectual property requires acquiring the correct legal safeguards. The plan may involve assessing the regions, assessing the security cost-effectiveness, and deciding on the schedule for submitting applications.
Creating and Documenting IP
Creating strong documentation processes is crucial for building a solid base for protecting intellectual property. Effectively recording the genesis and progress of innovations, concepts, and artistic products is essential in establishing ownership and upholding the legitimacy of intellectual property rights.
Training and Education on IP
Teaching staff, partners, and interested parties about the significance of intellectual property and their responsibilities in safeguarding it is frequently disregarded yet crucial. Effective training can prevent unintentional violations of intellectual property rights and promote a culture of intellectual property awareness.
Global IP Considerations
A comprehensive IP strategy for global organisations should take into consideration the diverse legal systems, cultural differences, and market conditions in different regions. Customising the plan to fit the specific needs of each area can enhance protective and enforcement efforts.
Defining Goals and Objectives
International organisations should consider different legal systems, cultural differences, and market conditions in various jurisdictions when developing an IP strategy. Customising the plan to meet the specific needs of each location can optimise protective and enforcement efforts.
Identifying IP Assets
The initial stage in creating an IP strategy involves recognising and listing all the intellectual property assets in an organisation or individual's collection. Possessions can range from patents and trademarks to copyrights, trade secrets, and industrial designs. Having a thorough list aid in grasping the extent and worth of these resources.
Navigate contracts with precision with our Commercial Contracts Management Training Register now!
Basic Steps to a Successful IP Strategy
The following are the basic five steps to successful Intellectual Property Strategy:
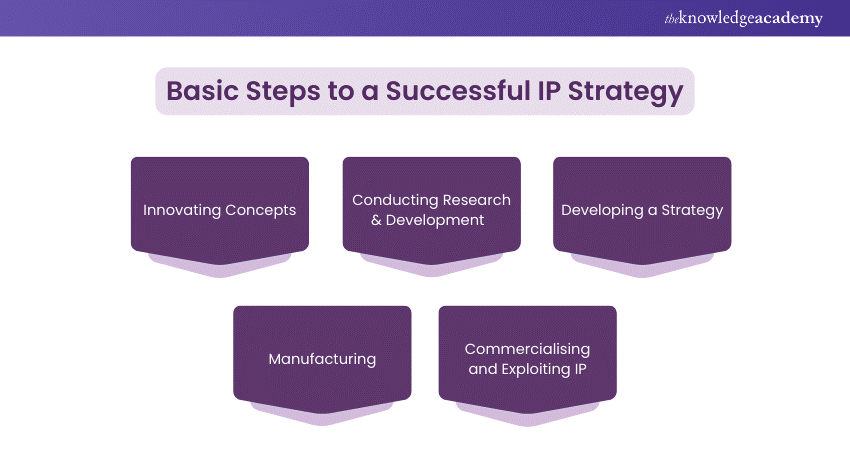
1) Innovating Concepts
To safeguard an idea or new concept, companies must ensure confidentiality. Employees should have binding Employment Contracts with strict confidentiality clauses. Additionally, any third parties involved in concept innovation, such as external designers, potential suppliers, or tooling manufacturers, should sign confidentiality or non-disclosure agreements (NDAs).
2) Conducting Research & Development
During the research phase, it is crucial to examine third party rights and conduct a freedom to operate search. Spending time and money on a concept that is already protected by another party is not worth it.
a) Conduct thorough patent and design searches with a trusted attorney.
b) Research online sources and study competitor actions to avoid potential disputes.
c) Ensure "freedom to operate" searches in all intended business territories.
d) Check for existing brand usage in target regions to avoid rebranding complications.
3) Developing a Strategy
Once you've decided to move forward with developing and launching the product, it's time to consider your Intellectual Property Strategy for it. The decision on the type of legal protection required will be based on various factors like the type of asset, how it will be used, the countries where it will be marketed, the longevity of the competitive edge, and other considerations.
a) All IP rights, except copyright, require active protection in each trading territory.
b) Copyright is automatically granted when original work is created and transcribed.
c) For trading in Europe, you must register your IP in the EU.
d) Post-Brexit, separate registrations are needed for the UK.
e) EU registrations offer protection only within EU countries.
f) They prevent other traders from importing goods into the EU. They cannot be enforced in non-EU countries, like the US.
4) Manufacturing
Tooling and production are crucial stages in the process of bringing a product to market. Ownership of the tooling by the business is crucial because if the manufacturer is the owner, it may be challenging to recover the moulds in case of a dispute later on.
a) Clearly specify IP ownership in manufacturing agreements.
b) Grant manufacturers only essential rights for production.
c) Limit rights to a specific product, timeframe, and quantity.
5) Commercialising and Exploiting IP
The majority of the work on your intellectual property is complete and it is important to have your protection plan ready. However, one must still consider that packaging can potentially attract intellectual property rights if the design is original. Make sure that any Branding on the packaging aligns with your registered trademarks and doesn't deviate from them.
a) Commercialisation agreements, including supply and distribution contracts, should: Clearly address IP rights.
b) Specify that all IP rights remain with the owner.
c) Exercise caution with distributors in new territories where IP protection may be limited: Ensure the agreement prohibits distributors from registering IP rights independently to "assist."
Be interview-ready! Explore the most common Contract Manager Interview Questions and sharpen your answers to land the perfect job.
Advantages of a Strong IP Strategy
The advantages of a strong IP strategies are:
a) Protection: An IP strategy shields valuable ideas and innovations from unauthorised use or replication.
b) Competitive Advantage: Strong IP can create a unique selling proposition (USP), distinguishing an organisation from its competitors.
c) Revenue Generation: Licensing or selling IP can open new revenue streams, enabling organisations to monetise their innovations.
d) Risk Mitigation: A robust IP strategy can reduce the risk of legal clashes and financial losses due to intellectual property infringements.
e) Attracting Investment: Well-protected IP assets can make an organisation more appealing to investors and potential partners.
f) Innovation Encouragement: An IP strategy can promote a culture of continuous innovation by rewarding creators for their contributions.
Take your career to the next level with Contract Management Certification Training. Learn to draft, negotiate, and manage contracts effectively. Enroll and begin today!
Challenges in Implementing an IP Strategy
Balancing protection and commercialisation present a strategic challenge. While securing IP can prevent misuse, it might also hinder partnerships or collaborations if potential partners feel constrained by the IP terms. Overcoming these challenges requires a well-coordinated approach that prioritises protection without stifling growth or innovation.
Conclusion
An Intellectual Property Strategy goes beyond mere protection; it enables businesses to secure their innovative assets and generate new value. By adhering to the key elements and steps detailed in this guide, companies can develop a robust IP strategy that promotes growth, drives Revenue, and offers a competitive edge in the global market
Lead with confidence in the world of innovation with our Intellectual Property Training Sign up today!
Frequently Asked Questions

The government body in charge of Intellectual Property (IP) rights such as patents, designs, trademarks, and copyright are known as the Intellectual Property Office. IPO is a government agency, funded by the Department for Business, Innovation & Skills.

The goal of an Intellectual Property (IP) Strategy is to enhance the worth of a company's IP assets while safeguarding them. An IP strategy must be incorporated into a business plan and must align with the business objectives.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Contract Management Courses, including the Intellectual Property Training, and the Commercial Contracts Management Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Business Contract.
Our ISO & Compliance Blogs cover a range of topics related to Business Contract, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your ISO and Business Management skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming ISO & Compliance Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Procurement Training & Certification Course
Procurement Training & Certification Course
Fri 14th Feb 2025
Fri 11th Apr 2025
Fri 13th Jun 2025
Fri 15th Aug 2025
Fri 10th Oct 2025
Fri 12th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


