We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +44 1344 203 999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
From the soothing voice of a sparrow to the magical sounds of an orchestra, Music is everywhere. Music has the power to touch our hearts, uplift our spirits, and speak to our souls. Every melody is constituted by fundamental concepts, namely the Music Theory. Understanding it is essential for Musicians to create melodies and harmonies that resonate with emotion and meaning.
According to Glassdoor, the average pay of a Musician in the UK is about £37,803 annually. So, it is a great career with high pay and perks. If you are passionate about pursuing this career, then this blog is for you. In this blog, you will learn What is Music Theory, its key elements, its benefits and how to learn it. Let’s dive in deeper to learn more!
Table of Contents
1) Understanding Music Theory and its essence
2) Key elements of Music Theory
3) Rudiments of Music Theory
4) Benefits of learning Music Theory
5) How to learn Music Theory?
6) Conclusion
Understanding Music Theory and its essence
Music Theory is the backbone of musical understanding, providing the essential framework for comprehending the intricacies of Music. It is the study of how music works, a set of principles and concepts that help Musicians and composers make sense of the sounds they create and hear. At its core, music is the language that enables us to communicate and analyse the elements that make up a piece of music.
Understanding the building blocks
Music Theory encompasses various concepts that serve as the building blocks of Music. These include Notes, Scales, Chords, Rhythm, Harmony, and more. Each element plays a decisive role in shaping the composition, allowing Musicians to convey emotions, tell stories, and connect with audiences.
Bridging creativity and structure
One of the most fascinating aspects of Music Theory is its ability to strike a balance between creativity and structure. While some might think that adhering to rules and principles stifles artistic expression, it actually serves as a guide that empowers Musicians to channel their creativity effectively. It provides a toolbox of techniques and ideas that can be applied to create diverse musical experiences.
Consider a composer crafting a symphony, Music Theory equips them with the knowledge to construct intricate melodies, harmonies, and dynamic shifts that evoke specific emotions. Similarly, a guitarist improvising solo benefits from understanding scales and modes, allowing them to explore different tonalities while staying in harmony with the accompanying Music.
Universal language of Musicians
Music Theory acts as a universal language that enables Musicians from different backgrounds to communicate and collaborate seamlessly. When a group of Musicians comes together, whether in a jam session or a full-fledged orchestra, their shared understanding of this theory allows them to synchronise their efforts. A jazz band, for instance, can smoothly transition between improvisational solos and group dynamics because they share a common vocabulary of chords, scales, and progressions.
In essence, this theory is the compass that guides Musicians through the vast landscape of musical creation and interpretation. It empowers artists to break down complex compositions, analyse their components, and appreciate the nuances that make each piece unique. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced Musician looking to refine your craft, diving into Music Theory enriches your journey. It does this by providing insights into the inner workings of the melodies and harmonies that resonate with us all.
Key elements of Music Theory
Music Theory is a vast and intricate domain that encompasses several essential elements. These elements serve as the foundational blocks for understanding the mechanics, structure, and emotions behind the music we hear. Here, let’s explore its key elements:
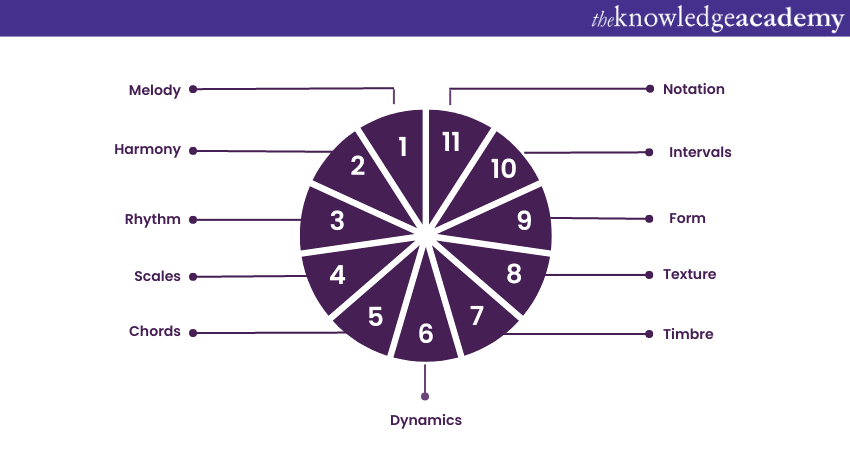
1) Melody: A melody is an arrangement of single notes that form a distinct musical line. It's the catchy tune that sticks in your head. Melodies play a pivotal role in conveying emotions and creating memorable musical phrases.
2) Harmony: Harmony refers to the simultaneous sounding of two or more notes to create a chord. It adds richness and depth to the music, often influencing how a piece makes us feel. Harmonies can evoke joy, sadness, tension, or resolution.
3) Rhythm: Rhythm is the organised arrangement of sounds in time, creating a sense of movement and groove. It encompasses the duration of notes, rests, and the patterns they form. Rhythm provides energy and drives a composition.
4) Scales: Scales are a sequence of ordered notes that form the basis of melodies and harmonies. They establish the tonality and mood of a piece. Common scales include major, minor, pentatonic, and chromatic scales.
5) Chords: Chords are formed by stacking multiple notes on top of each other. They establish the harmonic framework of composition, influencing its progression and emotional impact. Chords can be consonant (stable) or dissonant (unstable).
6) Dynamics: Dynamics refers to the varying levels of volume in Music. They add depth and contrast, enhancing the emotional impact of a composition. Terms like pianissimo (very soft) and fortissimo (very loud) denote different dynamic levels.
7) Timbre: Timbre, also known as tone colour, is the unique quality of a sound that distinguishes it from others. It's what makes a piano sound different from a violin, even when you play piano and the violin on the same note.
8) Texture: Texture refers to the way different musical elements interact to create a sense of depth. It can be thick or thin, simple or complex. Monophonic (single melody), homophonic (melody with accompaniment), and polyphonic (multiple independent melodies) are common textures.
9) Form: Form relates to the organisation of a musical composition. It outlines how different sections are arranged, repeated, and varied. Understanding form helps us follow the narrative of a piece and appreciate its coherence.
10) Intervals: Intervals are the distances between two notes in terms of pitch. They play a crucial role in creating melodies, harmonies, and chords. Intervals can be consonant (pleasant) or dissonant (clashing).
11) Notation: Music notation is the written representation of musical ideas. It includes symbols for notes, rhythms, dynamics, and more. It allows Musicians to reproduce compositions accurately and communicate musical concepts.
These key elements of Music Theory form the foundation for understanding and creating music. They intertwine to shape the Melodies, Harmonies, and Rhythms that touch our souls. By diving into each element, Musicians and enthusiasts alike gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate language of music and the emotions it conveys.
The rudiments of Music Theory
Music Theory, like any language, has its foundational elements, often referred to as rudiments. These fundamental components serve as the building blocks for understanding the complexities of Music. Let’s dive into the essential rudiments that provide the groundwork for Music Theory:
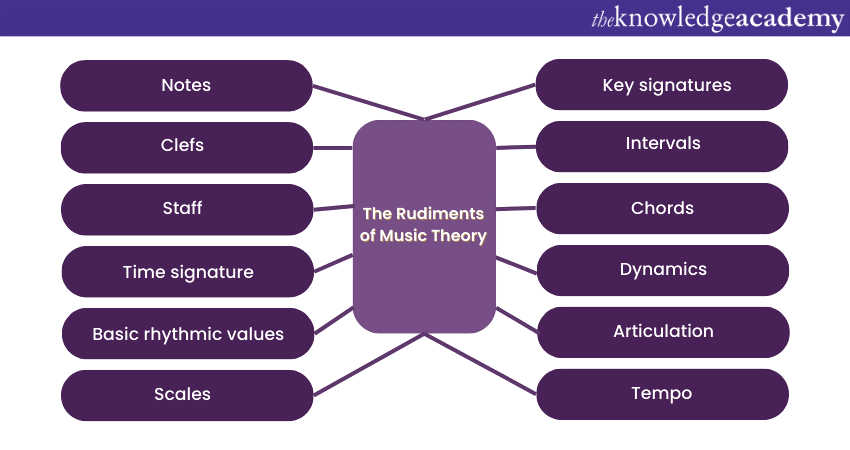
1) Notes: Notes are the basic units of music, representing distinct pitches. They are typically named after the first seven letters of the alphabet starting from A to G. The arrangement of notes forms melodies and harmonies.
2) Clefs: Clefs are symbols that indicate which pitch corresponds to a particular line or space on the musical staff. The treble clef and bass clef are some of the most common, representing higher and lower pitches, respectively.
3) Staff: The staff is a set of five lines and four spaces upon which musical notes and symbols are placed. It provides a visual representation of pitch and duration in music notation.
4) Time signature: The time signature consists of two numbers placed at the beginning of a piece of music. It denotes the amount of beats in a measure as well as which note value receives one beat and this establishes the rhythmic framework.
5) Basic rhythmic values: Rhythmic values determine the duration of notes and rests accordingly. Whole notes, half notes, quarter notes, eighth notes, and their corresponding rests are the fundamental units that create rhythm.
6) Scales: Scales are sequences of ordered notes that establish tonalities. The major and minor scales are the most prevalent, providing the foundation for melodies and harmonies.
7) Key signatures: Key signatures indicate the tonal centre of a piece and the specific notes that will be consistently altered (sharpened or flattened). They help musicians navigate through the various scales and harmonies.
8) Intervals: Intervals measure the distance between two notes in terms of pitch. They determine the relationships between notes, forming the basis for chords and melodies.
9) Chords: Chords are formed by stacking three or more notes on top of each other. They establish harmony and provide the foundation for accompaniment and harmonic progressions.
10) Dynamics: Dynamics indicate the volume levels in Music. Terms like piano (soft) and forte (loud) guide performers in conveying the desired intensity and emotion.
11) Articulation: Articulation symbols guide how notes are played, indicating whether they should be played smoothly (legato) or with separation (staccato), among other nuances.
12) Tempo: Tempo specifies the speed at which a piece is performed. Indications like allegro (fast) and adagio (slow) provide guidance on the intended pacing.
Mastering the rudiments of Music Theory lays the groundwork for a deep understanding of musical language. These essential components form the basis for communication between composers, performers, and listeners. By grasping these rudiments, Musicians gain the ability to interpret, create, and appreciate music with greater insight and precision.
Elevate your musical prowess with our Music Production Masterclass. Sign up today!
Benefits of learning Music Theory
Embarking on the journey of learning Music Theory offers various advantages that extend beyond simply playing or listening to music. Whether you're a budding musician or an ardent music lover, diving into this theory can significantly enhance your musical experience. Let's explore the diverse benefits that come with mastering the intricacies of this theory.
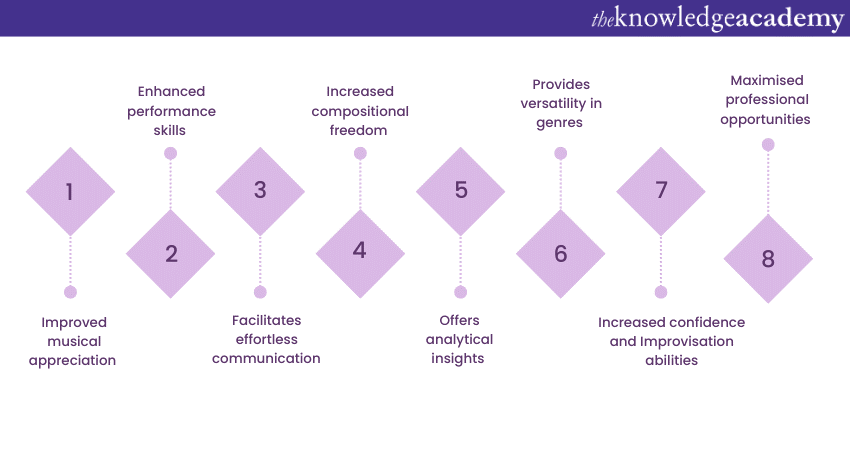
1) Enhanced musical appreciation: Understanding Music Theory deepens your appreciation for the art form. As you unravel the layers of harmony, rhythm, and structure, you'll be able to recognise the nuances that make each composition unique. This enriched perspective allows you to connect with music on a profound level, experiencing the emotional depth that the composer intended.
2) Improved performance skills: For performers, Music Theory acts as a guide that unlocks the secrets behind the scores. Knowing the theory behind the pieces you play empowers you to interpret them with greater accuracy and authenticity. You'll develop a stronger sense of phrasing, dynamics, and articulation, resulting in more expressive and captivating performances.
3) Effortless communication: Music Theory serves as a universal language for musicians. When collaborating with fellow musicians, being well-versed in theory ensures effective communication. Whether you're discussing chord progressions, key changes, or structural elements, a shared understanding of this theory streamlines the creative process and promotes seamless collaboration.
4) Compositional freedom: While some might associate Music Theory with rigid rules, it actually offers a framework for boundless creativity. By understanding the principles of harmony, melody, and rhythm, you can experiment with different musical ideas while maintaining a sense of coherence. This theory helps you make informed choices that enhance your compositions, allowing your imagination to flourish within a structured context.
5) Analytical insight: Analysing Music through a theoretical lens unveils its inner workings. You'll be able to dissect complex compositions, identifying recurring motifs, chord progressions, and structural elements. This analytical skill not only enriches your understanding of existing music but also informs your own compositional approach.
6) Versatility in genres: Music Theory transcends genres. Whether you're passionate about classical, jazz, rock, or electronic music, a solid foundation, in theory, equips you to navigate diverse musical landscapes. The principles you learn can be adapted and applied to different genres, expanding your musical horizons.
7) Confident improvisation: For improvisational musicians, Music Theory is a valuable toolkit. Understanding scales, modes, and chord progressions empowers you to improvise with confidence and coherence. You'll be able to explore new tonalities, experiment with variations, and create captivating solos.
8) Professional opportunities: Proficiency in Music Theory opens doors to various professional opportunities. Whether you're teaching music, composing for film and media, or working in music production, a solid understanding of theory enhances your credibility and skillset.
Learning Music Theory is not just a means to an end; it's a journey that transforms your relationship with Music. It enriches your listening experiences, elevates your performance abilities, and provides a comprehensive toolkit for creative expression. As you dive into the intricacies of Music Theory, you embark on a path of continuous growth and exploration. So, each new concept learned enhances your connection with the world of Music.
Embark on a melodic journey with our Piano Masterclass. Sign up today!
How to learn Music Theory?
Learning Music Theory is a rewarding endeavour that deepens your understanding of the language of Music. Whether you're a beginner or have some Musical background, here's step-by-step instruction for mastering this theory.
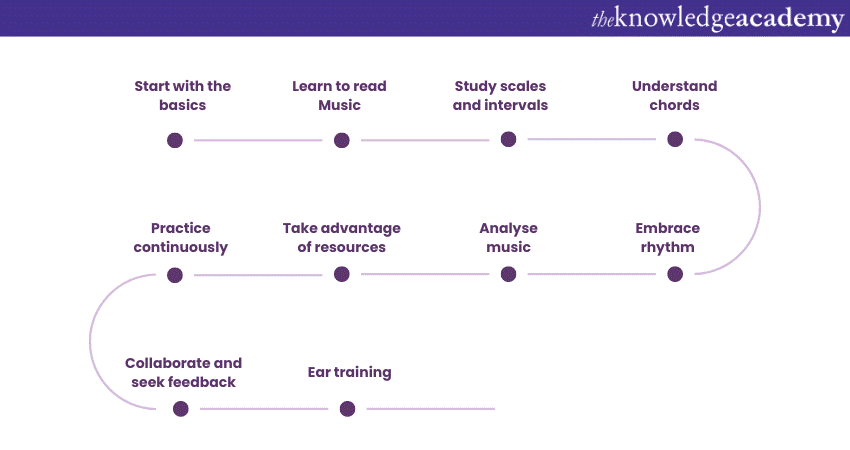
1) Start with the basics: Begin by familiarising yourself with the fundamental concepts of Music Theory. Understand the Musical alphabet, notes, and the layout of the Musical staff.
2) Learn to read music: Master the basics of music notation, including clefs, key signatures, time signatures, and rhythmic values. This will help you read and interpret sheet Music accurately.
3) Study scales and intervals: Dive into Scales and Intervals, the building blocks of melodies and harmonies. Start with major and minor scales, and grasp how intervals create different Musical distances.
4) Understand chords: Explore chord structures, chord progressions, and their relationships. Learn about major and minor chords, triads, seventh chords, and their inversions.
5) Embrace rhythm: Study rhythm patterns, time signatures, and syncopation. Practice clapping or tapping along with different rhythms to internalise them.
6) Analyse music: Listen to various Types of Music and analyse them using your newfound knowledge. Identify key signatures, chord progressions, and rhythmic patterns. This practice sharpens your analytical skills.
7) Take advantage of resources: Utilise resources such as textbooks, online tutorials, video lessons, and Music Theory apps. Websites like Musictheory.net offer interactive exercises to reinforce your learning.
8) Practice continuously: Apply theory to practical scenarios. Play instruments, compose melodies, and experiment with harmonies. Regular practice solidifies your understanding.
9) Collaborate and seek feedback: Collaborate with fellow Musicians or peers. Sharing ideas and receiving feedback can provide fresh perspectives and enhance your learning.
10) Ear training: Develop your ear by recognising intervals, chords, and melodies by ear. Ear training strengthens your ability to connect theoretical concepts to actual sounds.
11) Analyse famous compositions: Study the Music of renowned composers across genres. Analyse their compositions to understand how theory is applied creatively.
12) Create your own music: Apply your knowledge by composing your own music. Experiment with different chord progressions, melodies, and rhythmic patterns.
13) Engage with music communities: Join Music forums, attend workshops, or participate in local Music groups. Engage with others who share your passion can enhance your learning experience.
14) Join a course: Consider joining a formal Music Theory course, whether in person or online. Structured courses offer comprehensive learning, guidance, and opportunities for interaction.
15) Be patient and persistent: Learning Music Theory takes time. Stay patient and persistent, and celebrate your progress along the way.
Learning Music Theory is a dynamic and fulfilling journey. Remember that it's not about cramming rules but understanding the language that musicians use to communicate and create. Embrace the procedures, stay curious, and continue to explore this intricate world.
Conclusion
We hope you read and understand everything about Music Theory. It is the key behind melodies and harmonies. It empowers musicians to convey emotions and strengthens our bond with music's magic. Mastering it will open up the door to a rewarding career.
Unveil new passions and amplify your skills with our Hobbies & Interests Training. Sign up now!
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Music Production Course
Music Production Course
Fri 21st Feb 2025
Fri 25th Apr 2025
Fri 20th Jun 2025
Fri 22nd Aug 2025
Fri 17th Oct 2025
Fri 19th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


